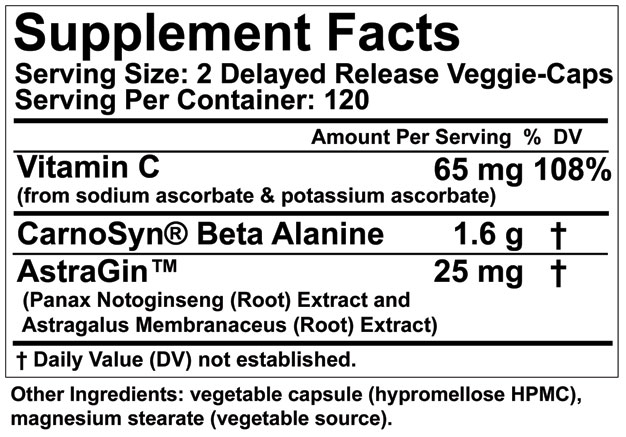
Carnage-ELITE™ combines the clinically tested & patented CarnoSyn® brand beta-alanine with the powerful nutrient enhancer AstraGin™. Carnage-ELITE™ is packaged in an easy to swallow, delayed release vegetable capsule which bolsters the formula’s potency by providing additional protection from destruction in stomach acid.*
- CLINICALLY DOSED CARNOSYN® BETA-ALANINE*
- ASTRAGIN™ ENHANCED TO INCREASE BETA-ALANINE ABSORPTION BY 26%*
- ADVANCED DR-CAP DELIVERY
- ZERO ARTIFICIAL INGREDIENTS
- TESTED GLUTEN FREE
- BANNED SUBSTANCE FREE**
AstraGin™ is a 100% natural food ingredient that has shown in cell, animal, and human studies to significantly improve the absorption of many essential life supporting and health promoting nutrients, such as amino acids, glucose, and vitamins into human cells. By allowing a greater amount of these nutrients to pass from the blood stream into the cells, AstraGin™ provides for truly improved bioavailability. AstraGin™ has been show in in-vivo studies to increase absorption of Beta-Alanine by 26% *
Research shows beta-alanine supplementation is the most effective way to boost intramuscular carnosine levels. Carnosine is a natural substrate in the production of Nitric Oxide (NO) that works by buffering fatigue & acid causing Hydrogen Ions (H+) created by intense exercise & heavy training. Increased muscular carnosine levels may allow you to train and compete more intensely for longer periods of time. Carnosine is primarily found in fast twitch muscle fiber responsible for explosiveness and power. By buffering hydrogen ions, carnosine may allow these fast twitch fibers to fire more efficiently and fatigue slower, increasing overall strength, power, endurance & performance.*
** Carnage-ELITE™ is made in the U.S.A in a cGMP facility and is formulated and manufactured without the use of any banned substances. Contains ZERO wheat, sugar, soy, starch, milk, eggs, fish, artificial colors, flavors or dyes. TESTED GLUTEN FREE!
Suggested Use: As an adult dietary supplement take two (2) DR-Caps twice daily. Take one serving 30-120 minutes prior to workout with water or a carbohydrate drink like INFINIT-E™. Take a second serving post workout with water or carbs. To buffer the harmless prickling, tingling or flushing sensation some users experience initially from beta-alanine, Carnage-ELITE™ may be taken in four (4) separate one (1) DR-Cap servings evenly spaced throughout the day or taken with food. Continue taking two (2) DR-Caps twice daily on non-training days. To support maximum intramuscular carnosine levels, Carnage-ELITE™ should be taken consecutively for a minimum of 30 days.
Stacking Suggestions: Carnage-ELITE™ may be stacked with most MST™ products including CRE-02™, Cordygen5™, Cordygen-NanO2™, Cordygen-VO2 ULTRA™, NitroCeps-ELITE™ or Agmatine-ELITE™.
Warning: This product is only intended to be consumed by healthy adults 18 years of age or older. Consult your physician prior to use, especially if you have a known medical condition. Do not take if pregnant or nursing or wish to become pregnant. Do not take this product if you have a known allergy to any of its ingredients. Store in a cool, dry place. Keep out of reach of children.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, prevent or cure any disease.
CarnoSyn® is licensed under one or more of U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,965,596, 6,426,361, 7,504,376 and 8,067,381, each of which is owned by Natural Alternatives International, Inc. (NAI). NAI is also the owner of the registered trademark CarnoSyn®
References
Abe H (2000) Role of histidine-related compounds as intracellular proton buffering constituents in vertebrate muscle. Biochemistry (Mosc) 65:757–765
Albani C, Blaser G, Geyer M, Schmutzer G, Bra¨hler E, Bailer H et al (2005) U¨ berpru¨fung der Gu¨tekriterien der deutschen Kurzformdes Fragebogens ‘‘Profile of Mood States’’ (POMS) in einerrepra¨sentativen Bevolkerungsstichprobe. Psychother Psychiatr Med 55:324–330
Artioli GG, Gualano B, Smith A, Stout J, Lancha AH Jr (2010) Role of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine and exercise performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42:1162–1173
Asatoor AM, Bandoh JK, Lant AF, Milne MD, Navab F (1970) Intestinal absorption of carnosine and its constituent amino acids in man. Gut 11:250–254
Baguet A, Reyngoudt H, Pottier A, Everaert I, Callens S, Achten E et al (2009) Carnosine loading and washout in human skeletal muscles. J Appl Physiol 106:837–842
Baguet A, Bourgois J, Vanhee L, Achten E, Derave W (2010a) Important role of muscle carnosine in rowing performance. J Appl Physiol 109:1096–1101
Baguet A, Koppo K, Pottier A, Derave W (2010b) Beta-alanine supplementation reduces acidosis but not oxygen uptake response during high-intensity cycling exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 108:495–503
Bakardjiev A, Bauer K (1994) Transport of beta-alanine and biosynthesis of carnosine by skeletal muscle cells in primary culture. Eur J Biochem 225:617–623
Bate-Smith EC (1938) The buffering of muscle in rigor: protein, phosphate and carnosine. J Physiol 92:336–343 Batrukova MA, Rubtsov AM (1997) Histidine-containing dipeptides as endogenous regulators of the activity of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-release channels. Biochim Biophys Acta 1324:142–150
Boesch C, Kreis R (2001) Dipolar coupling and ordering effects observed in magnetic resonance spectra of skeletal muscle. NMR Biomed 14:140–148
Boldyrev AA, Koldobski A, Kurella E, Maltseva V, Stvolinski S (1993) Natural histidine-containing dipeptide carnosine as a potent hydrophilic antioxidant with membrane stabilizing function. A biomedical aspect. Mol Chem Neuropathol 19:185–192
Decombaz J, Beaumont M, Vuichoud J, Bouisset F, Enslen M, Stellingwerff T (2011) The effect of slow-release b-alanine on absorption kinetics and paresthesia (abstract). Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:S2224
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K et al (2007) b-Alanine supplementation augments muscle carnosine content and attenuates fatigue during repeated isokinetic contraction bouts in trained sprinters. J Appl Physiol 103:1736–1743
Derave W, Everaert I, Beeckman S, Baguet A (2010) Muscle carnosine metabolism and beta-alanine supplementation in relation to exercise and training. Sports Med 40:247–263
Dunnett M, Harris RC (1995) Carnosine and taurine contents of different fibre types in the middle gluteal muscle of the thoroughbred horse. Equine Vet J S18:214–217
Everaert I, Mooyaart A, Baguet A, Zutinic A, Baelde H, Achten E et al (2011) Vegetarianism, female gender and increasing age, but not CNDP1 genotype, are associated with reduced muscle carnosine levels in humans. Amino Acids 40:1221–1229
Flancbaum L, Fitzpatrick JC, Brotman DN, Marcoux AM, Kasziba E, Fisher H (1990) The presence and significance of carnosine in histamine-containing tissues of several mammalian species. Agents Actions 31:190–196
Harris RC, Soderlund K, Hultman E (1992) Elevation of creatine in resting and exercised muscle of normal subjects by creatine supplementation. Clin Sci 8:367–374
Harris RC, Tallon MJ, Dunnett M, Boobis L, Coakley J, Kim HJ et al (2006) The absorption of orally supplied beta-alanine and its effect on muscle carnosine synthesis in human vastus lateralis. Amino Acids 30:279–289
Harris RC, Jones GA, Wise JA (2008) The plasma concentration-time profile of beta-alanine using a controlled-release formulation (Carnosyn) (abstract). FASEB J 22:701.9
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH et al (2007) Influence of beta-alanine supplementation on skeletal muscle carnosine concentrations and high intensity cycling capacity. Amino Acids 32:225–233
Hipkiss AR (2005) Glycation, ageing and carnosine: are carnivorous diets beneficial? Mech Ageing Dev 126:1034–1039
Hoffman J, Ratamess N, Kang J, Mangine G, Faigenbaum A, Stout J (2006) Effect of creatine and beta-alanine supplemen-tation on performance and endocrine responses in strength/power athletes. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 16:430–446
Hultman E, Soderlund K, Timmons JA, Cederblad G, Greenhaff PL (1996) Muscle creatine loading in men. J Appl Physios 81:232–237
Kendrick IP, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Kim CK, Dang VH, Lam TQ et al (2008) The effects of 10 weeks of resistance training combined with beta-alanine supplementation on whole body strength, force production, muscular endurance and body composition. Amino Acids 34:547–554
Kendrick IP, Kim HJ, Harris RC, Kim CK, Dang VH, Lamb TQ et al (2009) The effect of 4 weeks beta-alanine supplementation and isokinetic training on carnosine concentrations in type I and II human skeletal muscle fibres. Eur J Appl Physiol 106:131–138
Kley RA, Tarnopolsky MA, Vorgerd M (2011) Creatine for treating muscle disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD004760
Naressi A, Couturier C, Devos JM, Janssen M, Mangeat C, de Beer R et al (2001) Java-based graphical user interface for the MRUI quantitation package. Magma 12:141–152
Ozdemir MS, Reyngoudt H, De Deene Y, Sazak HS, Fieremans E, Delputte S et al (2007) Absolute quantification of carnosine in human calf muscle by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Phys Med Biol 52:6781–6794
Park YJ, Volpe SL, Decker EA (2005) Quantitation of carnosine in humans plasma after dietary consumption of beef. J Agric Food Chem 53:4736–4739
Parkhouse WS, McKenzie DC (1984) Possible contribution of skeletal muscle buffers to enhanced anaerobic performance: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 16:328–338
Sale C, Saunders B, Harris RC (2010) Effect of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine concentrations and exercise performance. Amino Acids 39:321–333
Sale C, Saunders B, Hudson S, Wise JA, Harris RC, Sunderland CD (2011) Effect of beta-alanine plus sodium bicarbonate on high intensity cycling capacity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182188501
Schroder L, Bachert P (2003) Evidence for a dipolar-coupled AM system in carnosine in human calf muscle from in vivo 1H NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 164:256–269
Shacham S (1983) A shortened version of the profile of mood states. J Pers Assess 47:305–306
Shen Y, Zhang S, Fu L, Hu W, Chen Z (2008) Carnosine attenuates mast cell degranulation and histamine release induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation. Cell Biochem Funct 26:334–338
Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene PR, Vagg PR, Jacobs AG (1983) Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory (Form Y). Consulting Psychologists Press Inc., Palo Alto, CA, p 36
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Mielke M, O’Kroy J, Torok DJ, Zoeller RF (2006) Effects of twenty-eight days of beta-alanine and creatine monohydrate supplementation on the physical working capacity at neuromuscular fatigue threshold. J Strength Cond Res 20:928–931
Zoeller RF, Stout JR, O’Kroy JA, Torok DJ, Mielke M (2007) Effects of 28 days of beta-alanine and creatine monohydrate supplementation on aerobic power, ventilatory and lactate thresholds, and time to exhaustion. Amino Acids 33:505–510
Stomach acid can destroy as much as 95% of a formula’s active ingredients. DR-Caps are thicker walled veggie capsules (plant derived hypromellose) designed to protect their contents from destruction in stomach acid for an extended period in comparison to standard gelatin or veggie capsules. We feel the added protection provided by DR-Cap delivery is highly valuable to the product’s potency and effectiveness.*
Yes, Carnage-ELITE™ is nearly twice as effective in comparison to the original Carnage™ product. Increasing the CarnoSyn™ (beta-alanine) dosage per capsule, adding AstraGin™ to supercharge bioavailability and protecting the formula with DR-Cap delivery puts Carnage-ELITE™ on a level all its own.
AstraGin™ is a patent pending, all-natural, plant based compound composed of highly fractionated Astragalus and Panax Notoginseng. In over 12 different in-vivo and in-vitro studies, AstraGin™ has demonstrated that it can significantly improve the absorption of critical nutrients.**
In multiple pre-clinical studies, AstraGin™ has shown that it can increase: **
- Amino acids absorption such as Arginine by 66.7%**
- Increases Beta-Alanine absorption by 26%**
- Vitamins absorption such as folate by 50.4%**
- Glucosamine absorption by 41.9%**
- ATP production by 18%**
** Information provided by NuLive Science
Studies show that beta-alanine is most effective when taken daily for at least 28 consecutive days. This allows intramuscular carnosine levels to build. We recommend taking Carnage-ELITE™ in the same manner.
120 DR-CAPS

240 DR-CAPS